Food Industry

Identify key emission reduction opportunities
Scope Three Action empowers food providers to take meaningful action to reduce their emissions. Whether you are a food retailer, manufacturer, bakery, or hospitality, the S3A’s tailored approach helps your business not only meet meaningful sustainability goals but also thrive in a rapidly evolving market that increasingly values climate-conscious practices.

Discover tailored solutions for your business
The first step is to understand your unique needs and challenges. By analysing your current situation—such as product portfolios, sales data, and supply chains—the S3A identifies the most impactful opportunities to lower your greenhouse gas emissions. Together, with the S3A, you establish a time-specific goal and create a clear roadmap to reduce your reliance on high-emission input and replace it with more climate-friendly ones.

Unlock expertise and resources
Scope Three Action provides you with resources such as training materials, best practices of supporting measures, and a network of trusted suppliers to support your transition. You get ongoing support from an expert team to ensure you have the tools needed to implement changes effectively.

Validate results and showcase success
As you report your progress against the targets, the S3A validates your data. Scope Three Action grant certification, providing credibility and transparency in your achievements and showcasing your commitment to sustainability. Scope Three Action provides support completely free of charge.
Ready to start your journey toward a greener future?
Reach out to us now and get expert guidance in reducing Scope 3 emissions!
Food sector companies will not only be heavily influenced by climate change but also play a pivotal role in it. By making smart choices, food providers can stand on the front line of the fight against climate change!
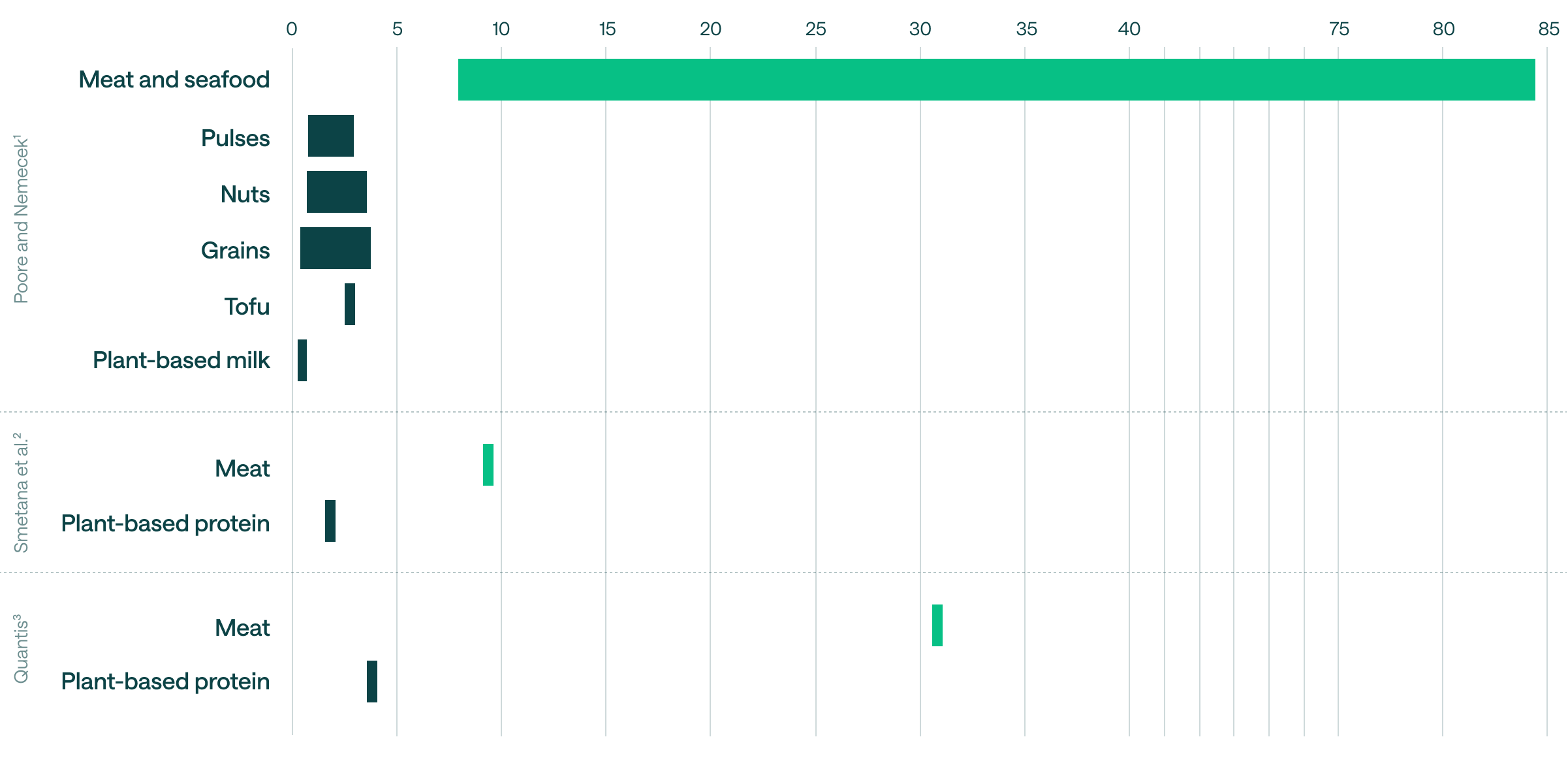
Unsurprisingly, the food itself is critical in lowering food sector companies’ carbon footprints. For example, in food retail, Scope 1 and 2 emissions—direct store operations or energy use—only account for about 7% of the total emissions associated with grocers. Meanwhile, 93% of their emissions come from Scope 3, which is generated across the supply chain. Meat and dairy account for half of these Scope 3 emissions. This doesn’t even take into account food production’s impact on soil degradation, water consumption, or eutrophication.
Worsening heat stress, volatile weather conditions, and forthcoming climate legislation and policies are anticipated to drive up costs in the food industry, particularly for animal-based products. Addressing these challenges and reducing GHG emissions is a crucial strategy for food companies to help build a sustainable future while mitigating risks and strengthening their market position.